Analyze 3D printing technology and its development prospects
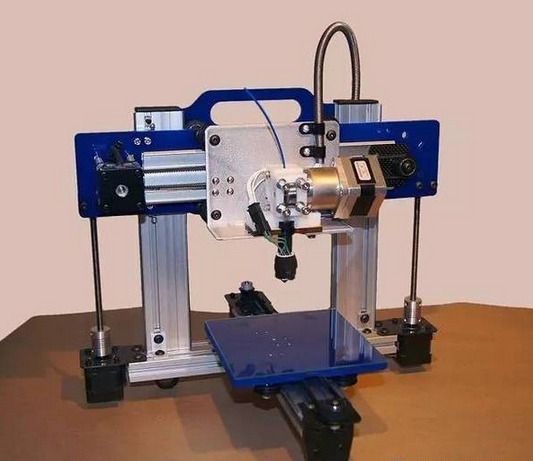
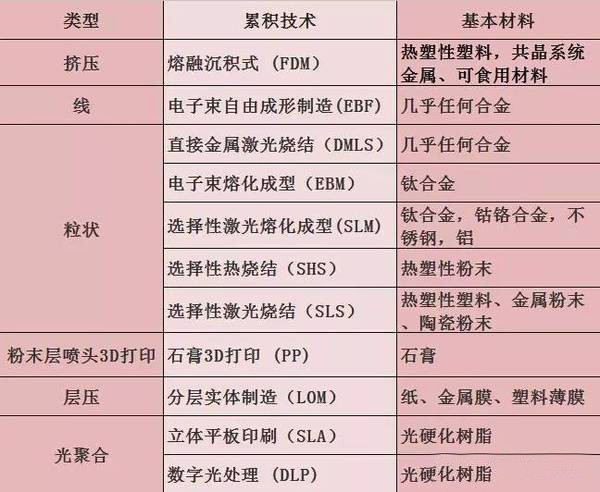
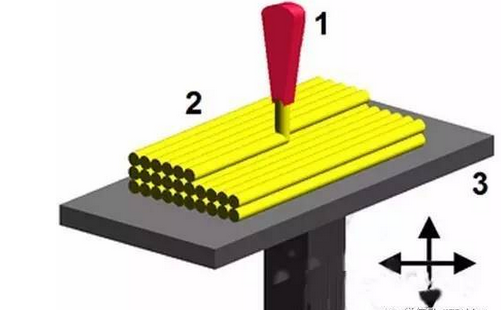
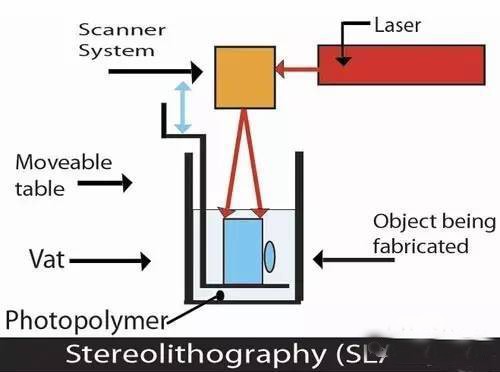
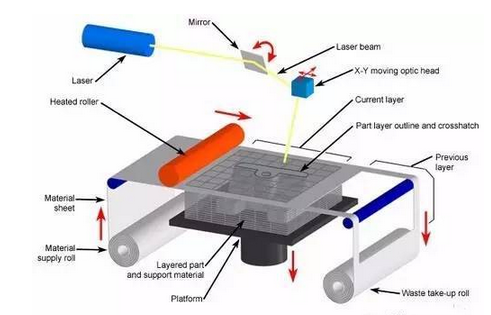
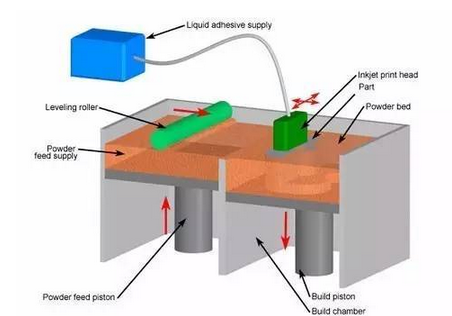
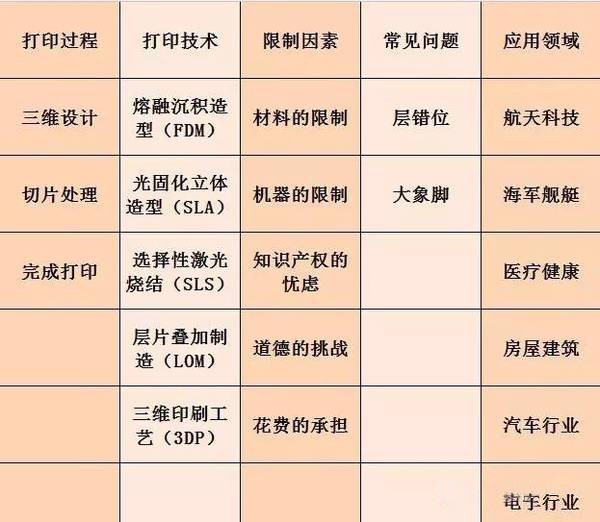
3D printing is a kind of rapid prototyping technology . It is a technique for constructing objects by layer-by-layer printing based on digital model files and using adhesive materials such as powder metal or plastic. 3D printing is usually done using a digital technology material printer. 3D printing history · In 1986, Charles Hull developed the first commercial 3D press. · In 1993, MIT obtained a patent for 3D printing technology. · In 1995, ZCorp of the United States obtained the sole authorization from MIT and began to develop 3D printers . · In 2005, the Spectrum Z510, the first high-definition color 3D printer on the market, was successfully developed by ZCorp. · In November 2010, the world's first car printed by a 3D printer, Urbane, came out. · 3D Print Picture On June 6, 2011, the world's first 3D printed bikini was released. · In July 2011, British researchers developed the world's first 3D chocolate printer. · In August 2011, engineers at the University of Southampton developed the world's first 3D printed aircraft. · In November 2012, Scottish scientists used human cells to print artificial liver tissue for the first time using a 3D printer. · In October 2013, the world's first successful auction of a 3D printed artwork called "The God of ONO". · In November 2013, SolidConcepts, a 3D printing company based in Austin, Texas, designed 3D printed metal pistols. · On January 16, 2017, the technology company Bellus 3D can fully capture high-resolution face 3D photos, which are 3D printed masks and real faces. · On April 7, 2017, the German sports brand adidas launched the world's first sneakers made of 3D printed soles. It is planned to start mass production in 2018 to cope with the fast-changing fashion trends and produce more customized products. 3D printing type list Common technical technology introduction 1. Fused deposition modeling ( FDM ): The FDM heating head heats the hot melt material (ABS resin, nylon, wax, etc.) to a critical state to make it semi-fluid, and then the heating head will be under software control. The two-dimensional geometric trajectory determined along the CAD moves, and the nozzle squeezes out the semi-flowing material, and the material instantaneously solidifies to form a thin layer with a contour shape. 2, Stereolithography ( SLA ): SLA light curing equipment will also slice the three-dimensional digital model of the object before starting to "print" the object. Then under computer control, the UV laser scans the liquid resin point by point along the contour profile of the part. The thin layer of resin that is scanned causes a polymerization reaction, which gradually forms a line from the dots, eventually forming a cured cross section of a thin layer of the part, while the unscanned resin maintains the original liquid state. When the layer is cured, the lifting table moves a layer thickness, and the surface of the cured resin is covered with a new layer of liquid resin for further scanning and curing. The newly cured layer is firmly bonded to the previous layer and is cycled until the entire part is prototyped. The SLA process is characterized by high precision and good surface quality, as well as parts that are particularly complex in shape (such as hollow parts) and particularly delicate (such as crafts, jewelry, etc.). 3. Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): First, a thin layer (sub-millimeter) of raw material powder is not laid on the workbench, and then the laser beam under computer control passes through the scanner at a certain speed and energy density. Scan by two-dimensional data at different levels. The laser-scanned powder is sintered into a solid layer of a certain thickness, and the unscanned portion remains as a loose powder. One layer is scanned and the next layer is scanned. First, the table is lifted according to the thickness of the cut-off layer of the object, and the powder-rolling roller flattens the powder again, and then starts scanning of the new layer. Repeat this way until all levels have been scanned. Parts can be obtained by removing excess powder and then subjecting it to appropriate post-treatments such as grinding and drying. At present, when this process is applied, wax powder and plastic powder are used as raw materials, and the process of bonding or sintering with metal powder or ceramic powder has not been practically applied. 4. Laminated object manufacturing (LOM): In the layer stacking manufacturing process, the machine heats the foil coated with the hot sol on one side by a hot roll, and the hot sol can be viscous under heating. Materials composed of paper, ceramic foil, metal foil, etc. are bonded together. Next, the upper laser stratifies the data according to the CAD model, and the laser beam is used to cut the foil into the inner and outer contours of the manufactured part. A new layer of foil is then applied and bonded to the undercut layer by a hot press and the laser beam is cut again. Then repeat the process until the entire part is printed. It is not difficult to find that the LOM process still has the shadow of traditional cutting. Rather, it does not use a large piece of raw material for overall cutting, but instead divides the original part model into multiple layers and then performs layer-by-layer cutting. The 3D printer that was first developed in the era of Beijing Taier is also the 3D printer of LOM technology. However, because of the use of paper as raw material, the risk of ignition by laser cutting is limited, and the application is limited. Therefore, the era of Taier later turned to the FDM process. 5, 3D printing (3D printing, 3DP): From the perspective of working methods, 3D printing is the closest to traditional 2D inkjet printing. Like the SLS process, 3DP also makes parts by bonding the powder into a whole, except that it is not bonded by laser melting, but by a spray from the nozzle. Under the control of the computer, the nozzle is operated according to the two-dimensional data of the model section, and the adhesive is selectively sprayed at the corresponding position to finally form a layer. After the bonding of each layer is completed, the forming cylinder is lowered by a distance equal to the thickness of the layer, the powder cylinder is raised by a height, the excess powder is pushed out, and pushed by the spreading roller to the forming cylinder, which is flattened and compacted. This cycle until the bonding of the entire object is completed. 3D printing overview   3D printing common problems and solutions First, 3D model printing layer fault Solution: 1, the slice model is wrong. 2. The nozzle moves too fast. 3. The nozzle is forcibly blocked in the middle of printing. 4. The voltage is unstable. 5. Mechanical problems. 6. Motherboard problem. Second, the elephant's foot (when the bottom layer of the model protrudes slightly outward, this phenomenon is called "like the foot")    Solution: 1. Balance the print platform temperature and fan speed. 2. The printing platform is leveled. 3. Check the nozzle height. 4. Chamfer model design. Chair Set,School Canteen Chairs,School Classroom Chairs,Classroom Sketching Chair AU-PINY FURNITURE CO., LTD , https://www.au-piny.com